One of the core tenets of Bitcoin is to avoid trust and always verify. To do this, you should practise self-custody and reduce exposure to intermediaries. While this is the intended use for Bitcoin, the reality is very few people have taken the time to use the asset and the network in a trustless manner.
Incorporating intermediaries into your Bitcoin experience is a trade-off; you might gain convenience or avoid technical mistakes as a novice user, but you take on the risk of the counter-party. This is a decision that has consequences, as many who are in custody with exchanges and digital asset custodians found out and continue to find out the hard way.
As a Bitcoiner who wants to take full advantage of the network, your first step should be to learn and practice self-custody; once you’ve secured your coins, you can start to explore other facets of non-custodial Bitcoin, like spinning up a full node.
Running a Bitcoin node is optional but remains essential because it helps to secure the network and verify transactions. When you run a node, you avoid any middlemen between you and the chain; you read the transaction data and act as a check on the network to ensure that transactions are valid and that no one is trying to double-spend coins.
You are also helping to decentralise the network by providing a copy of the blockchain to other nodes should nodes fall out of sync and require a copy of the chain.
Bitcoin is designed to run its software with very low tech, giving you more options and allowing as many people as possible to access the network without help from others. You could run a node and a wallet on an old laptop or low-powered device like a Raspberry Pi or set up a virtual machine with Nix Bitcoin.
The Cloud is just someone else’s computer.
If you don’t have the time or hardware to run a Bitcoin node, you can always lease computation from a service provider, an action we’ve become all too familiar with, even if we don’t realise it. If you’re paying for iCloud storage, you’re using AWS; if you have documents saved on Google Drive, you’re using Google Cloud; and if you’re using any Office 365 products, you’re an Azure customer by default.
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
So, instead of purchasing additional hardware, you can pay a service provider to store files or run programs and have access to them on demand. Cloud computing allows anyone with an account to spin up a virtual machine to run almost anything, including a Bitcoin node.
What is a Bitcoin cloud node?
A Bitcoin Cloud Node is a node hosted with a cloud provider rather than on your own hardware. This means that you can run a Bitcoin node without owning the physical hardware or worry about setting up and maintaining your server hardware and software.
There are a number of different cloud providers that offer Bitcoin Cloud Nodes, including Google Cloud Platform, Amazon Web Services, and Microsoft Azure. These providers typically offer a variety of different node configurations, so you can choose the one that best meets your needs and budget.
To run a Bitcoin Cloud Node, you simply need to create an account with a cloud provider and select a node configuration. The cloud provider will then set up and maintain the node for you. Once the node is up and running, you can connect to it using a Bitcoin wallet or other Bitcoin software.
There are a number of reasons why you might want to run a Bitcoin Cloud Node. Some of the benefits include:
- Convenience: Bitcoin Cloud Nodes are very convenient to set up and maintain. You don’t need to worry about any of the technical aspects of running a node, such as hardware setup, software installation, or security.
- Scalability: Bitcoin Cloud Nodes are scalable, so you can easily increase or decrease the resources allocated to your node as needed. This is useful if you need to handle a lot of traffic or store a large amount of data.
- Reliability: Bitcoin Cloud Nodes are typically hosted in high-availability data centres, so you can be confident that your node will be up and running even if there are problems with your own internet connection or hardware.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to running a Bitcoin Cloud Node. One concern is that you are trusting a third-party provider with your Bitcoin data. Another concern is that Bitcoin Cloud Nodes can be more expensive to run than traditional nodes.
Overall, Bitcoin Cloud Nodes can be a good option for people who want to run a Bitcoin node without having to worry about the technical aspects. However, it is important to weigh the benefits and drawbacks before deciding whether or not to run a Bitcoin Cloud Node.
Additional reasons why you might want to run a Bitcoin Cloud Node include:
- Improved uptime: By running with a data centre, you can fall back on their redundancy protocols and ensure little to no downtime, as you might have by kicking out the modem at home by accident.
- Fallback node: When you run a full node, you can verify all transactions and blocks yourself, but it doesn’t mean your node can’t fail; hardware failure, internet or electricity outages could render your node offline and having a cloud node to fall back on can be a viable option.
- No physical hardware limitations: When using a third-party service like a cloud node, you can easily access more resources and pay for the additional computation or capacity instead of buying mode RAM or a bigger hard drive.
Using a dedicated cloud node service
Cloud computing has its advantages, and access has never been easier with big tech providers like Amazon, Google and Microsoft all competing with their offerings, but from personal experience, it is still not a service for the average user. If you’ve ever logged into a cloud service provider account, you’ll know what I am talking about, especially AWS.
The learning curve is steep, and running a virtual machine (VM) in a cloud environment can be challenging for a novice, especially if you require some networking experience. While several resources are available to help you get started with your preferred cloud provider, sifting through applicable tutorials or YouTube videos is not the best onboarding experience.
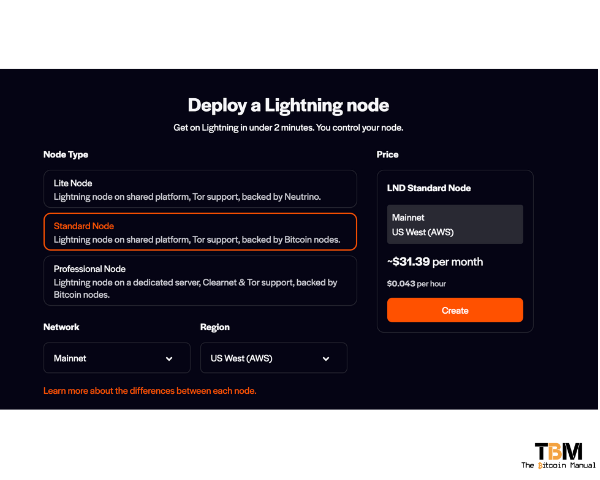
If you are considering running a Bitcoin Cloud Node, and that’s all you want to do, then a node service provider like Voltage might be the better option. Instead of having to do all the configurations for your virtual machine, you can opt for a service provider to abstract that complexity and give you a simple interface to select from presets.
Cloud node service providers provide:
- Easy setup and maintenance: Voltage takes care of all the technical aspects of setting up and maintaining your node, so you don’t have to worry about anything.
- Scalability: Voltage nodes are scalable, so you can easily increase or decrease the resources allocated to your node as needed.
- Reliability: Voltage nodes are hosted in high-availability data centres, so you can be confident that your node will be up and running even if there are problems with your own internet connection or hardware.
- Tor integration: Voltage nodes are integrated with Tor by default, which means that your node’s traffic is anonymized and encrypted. This makes it more difficult for attackers to track your node or your activity on the Bitcoin network.
- Support for the Lightning Network: Voltage nodes can be used to run Lightning Network nodes, which allows you to make fast and cheap Bitcoin payments.
- Flexibility: Voltage offers a variety of node configurations to choose from, so you can find the one that best meets your needs and budget.
- Customer support: Voltage offers excellent customer support, so you can get help if needed.
A cloud node is not for everyone.
But I thought we should remove all intermediaries; why would I want to run a cloud node? Yes, of course, if your goal is total privacy and total control over your Bitcoin interactions, then having a DIY setup is the ideal option for you.
If you’re trying to run a profitable routing node, you also need to make a decision: Do you opt for closely managing your node but saving on that monthly running cost, which would eat into your profits, or do you have a large enough node that your earnings can cover your cloud bill and still leave you in profit.
Perhaps you start on a home node, and once you build up capital and confidence in your ability to generate a yield on Lightning, you can move your operations to a cloud node.
Who would use a cloud node?
A cloud node is not for everyone; it serves a specific use case and caters to a specific set of customers.
If you are considering running a node at home or for your business and you’re wondering why to pay a cloud provider every month versus running your own node for a once-off payment, you might want to consider the following use cases.
Bitcoin application developer/service provider
Bitcoin app developers need to be able to provide a reliable service, and depending on their application, they might need to support not only Bitcoin but layer two networks as well. Cloud nodes provide them with a convenient and affordable way to support all their customers and maintain a reliable infrastructure while they scale their operations.
Bitcoin eCommerce store
Bitcoin businesses such as eCommerce stores and merchants need to be able to verify transactions and blocks quickly and reliably. Cloud nodes can provide them with the performance and scalability they need to manage their Bitcoin payments without handing over custody of their funds.
Bitcoin P2P trader
As a P2P trader, you might want to run only some of your trades through your local node, either due to the speed of running on Tor or giving away additional privacy details. Instead, a cloud node could provide a better and more reliable base of operations as you focus on moving liquidity to different parts of the network and exploiting arbitrage opportunities.
Do your own research.
If you want to learn more about cloud nodes, use this article as a jumping-off point and don’t trust what we say as the final say. Take the time to research, check out their official resources below or review other articles and videos tackling the topic.




