The price of bitcoin tends to take up most of the discussion and attention, especially with those new to the asset, and some even become obsessed with it. Riding the highs and lows that are bitcoin volatility can be an emotional rollercoaster, and becoming a constant price checker won’t help your situation.
If you have been one of those who pay a lot of attention to the price, you’ve likely used different services to check the price. It could be within a Google search, a block explorer, a price aggregating website or an exchange. If you pay close enough attention to the various data sources, you’ll notice slight variations in pricing depending on the source you’re using.
So why are bitcoin prices different across various exchanges?
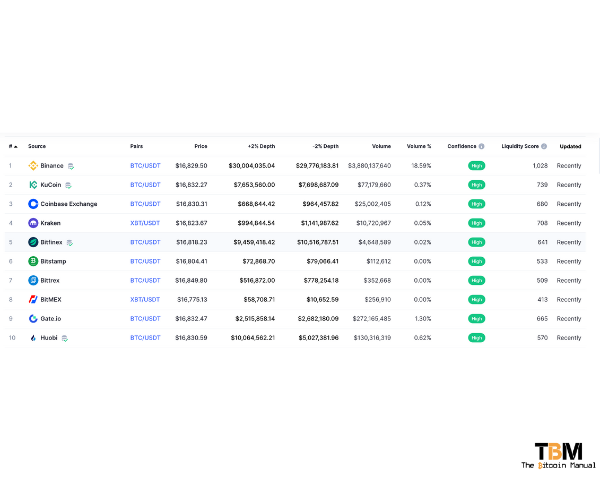
Comparing bitcoin prices
If you compare bitcoin across exchanges at any time on any given day, chances are you’ll see differences in its price. The standard difference between prices ranges between 1-2%, but sometimes even 4-5% on busy trading days. In certain extreme cases like the Kimchi premium, you can even find prices that are 10-15% higher or lower than the majority of exchanges.
How can a single asset trade at two different prices?
Price differences exist because markets are not truly efficient; despite the leaps and bounds made in improved settlement with stablecoins and better banking relations as the industry matures, prices still have a band in which it trades.
The price of bitcoin varies slightly across markets due to the different platforms involved, how their banking regulations and laws work, the clearing of funds on the platform, the fees that bitcoin exchanges charge investors, as well as the varying levels of trade volume, liquidity and access to bitcoin.
Varying prices across exchanges also create what’s known as an arbitrage opportunity, which some traders take advantage of with the hope of profiting, but also provide a valuable service in that they move liquidity to where it is needed most.
No set price
The first point to address is that in bitcoin, there is a distinct lack of any standard pricing or market actor conducting operations to ensure specific price stability. Bitcoin has no recognised standard price or price range; the price is up to what the market is willing to pay at any particular time.
Those looking to buy or sell bitcoin will find that, as is the case with all commodities, supply and demand varies depending on the market and the time you decide to take action. While the price of bitcoin is also affected by the fiat pair, you’re looking to trade in such as USD, EUR, CAD, JPY or GBP, for example.
Each country has its own centralised exchanges that try to secure bitcoin liquidity to be traded in a local currency. Since each fiat currency has its own price range, that also introduces additional pricing complexity.
Transaction costs
Every exchange platform is a business, they exist to make money, and It is important to remember that for them to make money, they need to charge fees. If several fees, such as the deposit, withdrawal, transaction fees, and usage fees, all add up to surpass the value difference of the actual trade, then the arbitrage opportunity is nullified.
Liquidity
Liquidity refers to the ability to exchange bitcoin without substantially shifting its price in the process, and the ease with which an asset can be converted to fiat. The easier it is to convert the asset to cash, the more liquid the asset is.
It can be frustrating when one has orders delayed due to a lack of liquidity and you either have unfilled or partially filled transactions at your ideal price point. Hence, the demand and supply levels of bitcoin on exchange plays an important role in what becomes the ask and bid price. The ask price and bid price difference is the spread; hence, the higher the liquidity, the lower the spread, and the lower the price.
Exchange volume
Volumes on exchanges are limited by the amount of production in new coins and, of that, what percentage miners are willing to place on the market. Depending on the liquidity of the exchange, it can attract miners or sellers to their platform due to the seller’s confidence that there will be little to no slippage when selling their bitcoin.
If the exchange hasn’t got enough volume, it can command higher prices because of the convenience it offers sellers. They are willing to sell at a higher price because traders can realise their gains easier.
If you have a look at bitcoin trading volume, it is normally much higher on the larger exchanges, such as Binance and CoinBase, while smaller exchanges see less volume. This difference in supply and bids on the order book can affect the price of bitcoin across those exchanges.
Can I profit from the differences in prices on crypto exchanges?
Arbitrage opportunities in bitcoin are mainly employed by short-term day traders and professional investors looking to make short-term profits, but that doesn’t mean some arbitrage trades don’t take long to execute or that there won’t be repeat trades.
While anyone can participate in an arbitrage trade should they have an account on exchanges, they could buy on one to sell on the other. Still, it is more suited to professional traders that have access to larger pools of liquidity to exploit these price discrepancies properly.
Additionally, certain arbitrage trades might require international banking services to clear non-bitcoin-based funds faster between countries if stablecoins are not an option. A situation that lends itself to institutional traders rather than retail traders who might have limited access to exchanges and global liquidity.
Having natural price discovery
For those who don’t have the time and energy to start actively seeking arbitrage opportunities, there’s still good news. When other investors employ arbitrage strategies, the prices of cryptocurrencies across exchanges become more aligned. Essentially, supply and demand meet in the middle at the spot price — the asset price agreed upon by both the buyer and seller at a given time and place, usually on a specific exchange.
This process, known as price discovery (in all of finance — not just bitcoin), helps determine the true value of the asset in question.
A combination of market forces
Cryptocurrency exchanges typically show slightly different prices as they are independent businesses all selling you a product and looking to profit from your purchase.
Since there are no rules mandating how bitcoin should be priced but rather the global demand, exchanges need not be connected, nor have their liquidity sourced from the same place. Exchanges may be sourcing directly from miners; others might buy from other exchanges and OTC desks or have their own mining operations to provide liquidity.
Due to the difference in the sourcing of liquidity and the demand for the bitcoin on the exchange order book, you will see variations in pricing as market participants try to meet at a certain price. So what you see is not so much of a “timing” or “delay” issue but simply natural differences across exchanges.
In summary, the volatility, location, speculation, demand and supply, volume and all the associated factors add to the varying bitcoin prices between exchanges.
How do you hold your bitcoin?
Where do you check the price of bitcoin? Have you noticed price differences in the past? How do you source the cheapest bitcoin? Do you buy bitcoin on an exchange? Do you smash buy or use limit orders?
Let us know in the comments down below.




