Many of us who discovered Bitcoin feel like kicking ourselves for not getting in on the early gold rush, where it was possible to mine coins on a desktop computer or laptop.
As early miners fried their CPUs for Bitcoin, they eventually graduated to GPUs, and around 2011, most mining powers started coming from CPU miners who enjoyed a 30x increase in computing power versus CPU miners.
The days of Bitcoin GPU mining are long gone; you could still do it today and make a few satoshis, but you’d be sending your GPU to an e-waste graveyard sooner than it should have and probably end up with a negative return on investment.
If you plan on mining, you need to have specialised equipment; there are tonnes of different ASICs on the market, and depending on your price range, you can pick up a new one or a second-hand one and hope there’s still enough life left in it, to kick out some coins.
So, if Bitcoin mining is out of the question, what’s happening with GPUs today?
GPU’s still have plenty of uses
Big data requires immense processing power; think of GPUs as part of the refinery process of large data sets. Just like we have massive refineries for physical commodities like oil and uranium, digital information requires vast amounts of refining through processing power. Our modern society demands more processing power to drive business operations and leverage the datasets we create in real-time.
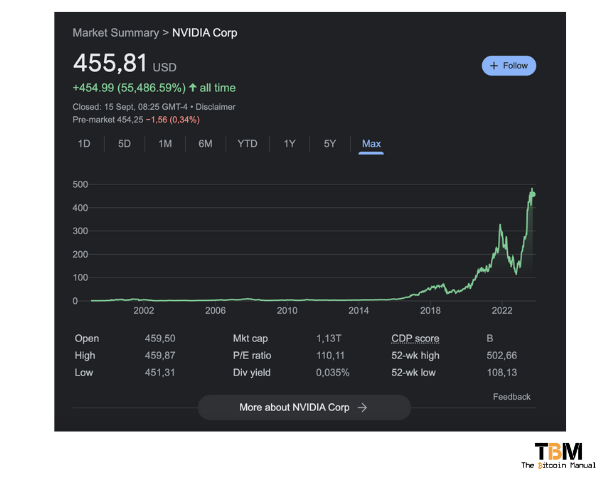
The demand for processing power has seen NVIDIA become a multi-billion dollar company, and they’re showing no signs of slowing down; even with chip manufacturers riding this wave, the market demand for GPUs keeps rising.
While almost every business is using GPUs in some way, shape or form, the industries that seem to be the most data-hungry are:
- Gaming: The gaming industry is one of the largest and fastest-growing markets for GPUs. GPUs are used to power high-performance graphics in video games, and the demand for better graphics is constantly increasing.
- Virtual reality and augmented reality: Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are two emerging technologies that are expected to drive demand for GPUs. VR and AR applications require high-performance graphics and processing power, and GPUs are well-suited for these tasks.
- Machine learning: Machine learning is a rapidly growing field that is being used in a wide variety of applications, including image recognition, natural language processing, and fraud detection. GPUs are well-suited for machine learning applications because they can perform complex calculations quickly and efficiently.
- Data science and analytics: Data science and analytics are also two growing fields that are driving demand for GPUs. GPUs are used to process large amounts of data quickly and efficiently, which is essential for data science and analytics applications.
- Cryptocurrency mining: Certain altcoin mining projects that use proof of work and don’t have the competition that Bitcoin has can still use GPUs to generate the hashes to support their network.
Getting access to GPUs
As an individual user, an application or a business that need access to computing power, you can opt for building up your own infrastructure or leveraging third parties for a fee. Depending on your needs and limitations like:
- Your budget: The cost of GPU processing power can vary depending on the provider and the type of GPU hardware you need.
- Your needs: How much GPU processing power do you need? How often do you need it?
- Your expertise: How comfortable are you with using cloud computing platforms or GPU-as-a-service providers?
You will likely opt for one of the following:
Local GPU clusters
If you have the budget and technical expertise, you can also set up your own local GPU cluster. This can be a good option if you need to run GPU-intensive applications on a regular basis.
Cloud computing platforms
Cloud computing platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, offer GPU-powered virtual machines that you can rent on demand. This is a convenient and flexible option, as you can scale up or down your GPU usage as needed.
GPU-as-a-service providers
There are a number of GPU-as-a-service providers that offer GPU-powered compute resources that you can rent on demand. These providers typically offer a wider range of GPU options than cloud computing platforms, and they may be a good option if you need specialized GPU hardware.
Temporary GPU demand is mostly handled by large data centres that have pretty strict pricing structures that make it hard for certain businesses and business models to leverage. These data centres have fixed costs they need to cover, and they’re looking for scale; this leaves a large portion of the market underserviced or unserviced.
This is where GPU-SAAS businesses could come in to fill the gap with a little help from WebGPU.
What is WebGPU?
WebGPU is a new API that exposes the capabilities of GPU hardware for the Web. It is designed to be more efficient and flexible than the existing WebGL API, providing access to more advanced GPU features. WebGPU is still under development, but it has been adopted by major browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, and Edge, with the expectation that it will become the standard API for GPU programming on the Web.
Some of the benefits of using WebGPU:
- Performance: WebGPU is designed to be more efficient than WebGL, which can lead to better performance for graphics-intensive applications.
- Flexibility: WebGPU provides more flexibility than WebGL, which allows developers to create more complex and demanding applications.
- Access to advanced features: WebGPU provides access to more advanced GPU features, such as ray tracing and machine learning.
If you are developing a graphics-intensive web application, consider using WebGPU. Some of the applications that can benefit from using WebGPU:
- 3D games: WebGPU can be used to create high-performance 3D games that are comparable to those that are available on desktop and mobile platforms.
- Virtual reality: WebGPU can be used to power virtual reality experiences that are immersive and realistic.
- Machine learning: WebGPU can be used to accelerate machine learning applications, such as image recognition and natural language processing.
- Scientific computing: WebGPU can be used to accelerate scientific computing applications, such as simulations and data analysis.
What does GPUtopia do?
WebGPU allows you to provide your GPU power to others, but why should you give up your idle machine, electricity and internet connection needed to do this for free? You shouldn’t have to, but with fiat payment rails, it doesn’t make much sense to charge for these micro-jobs. To make a scalable marketplace for computing power, you need money globally that can settle in an instant, money that runs on a network that is programmatic and can handle millions of microtransactions.
GPUtopia is a computer processing marketplace that aims to bring those looking for additional computation together with those with spare computation to sell.
- 💻 SELLERS rent out their GPU computing in exchange for Bitcoin.
- 🛍️ BUYERS pay Bitcoin to use GPU compute for AI training or inference.
By building a marketplace for GPU computing, GPUtopia could unlock millions of GPUs around the world currently sitting idle and distribute income around the world as users try to source the cheapest computing power available.
Users with idle computing power can lease out their computers at any time for a fee and earn rewards in Bitcoin via the Lightning Network.
How does it work?
GPUtopia uses a portion of your computer’s GPU via WebGPU, so you’ll need a compatible browser first. Let’s say you’re using a Chromium browser like Chrome or Brave; your next step would be to download the Alby wallet browser extension, as you will need it to create an account.
Once you have Alby installed and created an account with GPUTopia, you will need to download the AI model the network is selling. This could be a large language model like ChatGPT or an image processing model like MidJourney.
The model of choice will downloaded to your device and stored in your browser’s cache. This will take a few minutes to download, then ~20 seconds to load from cache on future visits.
Once you’ve got the model loaded, the GPUtopias system marks your device available to receive inference jobs. Buyers of processing power will then submit jobs via the marketplace; the job may take ~5-30 seconds to complete, depending on your GPU and the job size.
Getting paid in bitcoins for my GPU to work on AI jobs!
— Adam Mashrique (@sakak_musdom) September 13, 2023
Everything runs in the browser thanks to WebGPU, WebLLM and @getAlby https://t.co/Ehn07tu9oC pic.twitter.com/PtRgRLUSqC
When your computer finishes the inference job, it sends that back to GPUTopias, and you are paid instantly in Bitcoin via the Lightning Network to your Alby wallet. If you’re unfamiliar with the Lightning Network, use Albys’ custodial wallet. Alternatively, you can use Alby to interface with your Lightning Node for a non-custodial experience in stacking sats.
The Lightning Network allows buyers and sellers to conduct micropayments so you only pay for what you use, and settlement is instant; in essence, marketplaces like GPUtopia and protocols like LangChainBitcoin can create a secondary market for GPU mining.
Do your own research.
If you want to learn more about GPU marketplaces, use this article as a jumping-off point and don’t trust what we say as the final say. Take the time to research, check out their official resources below or review other articles and videos tackling the topic.